Decision Networks
Essentially, decision networks are extensions of Bayesian networks.
Bayesian networks decrease the number of variables leading to the result.
Decision Networks (aka. influence diagrams) is to combine BN with action and utility nodes to figure out how to get a specific result.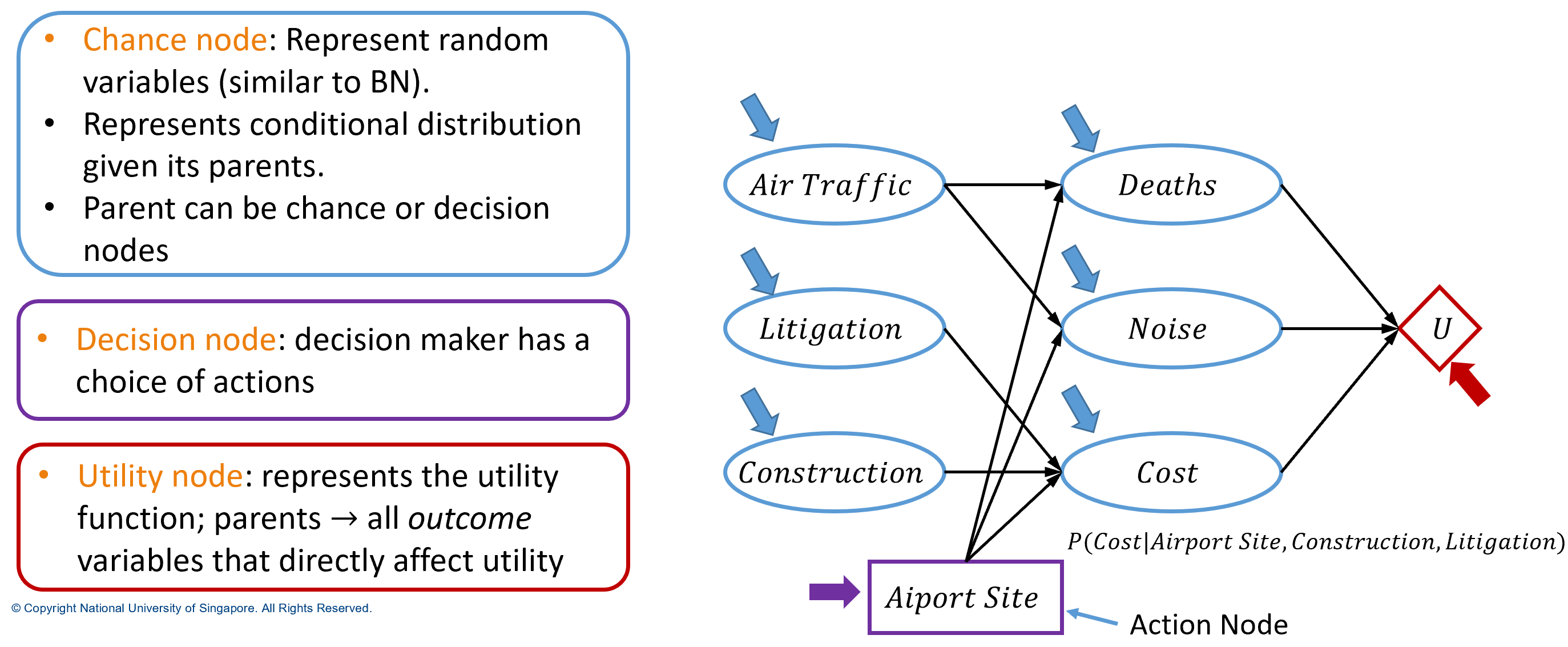
A simplified form is to eliminate chance nodes that represent outcome state, which means that action node and current state are directly connected to the utility node.
Utility node represents the expected utility associated with each action and is then associated with the action-utility function or 𝑄-function(Q: quality of action)
In this lecture we view Probability Inference(refer to Uncertainty in AI) as a black box and use tool to solve it.
Value of information
Assume exact evidence can be obtained about variable $E_j$;
To compute value of perfect information (VPI):
- Given current evidence $e$, expected utility with current best action $a$:
- Value of the best new action after $E_j=e_j$ is obtained:
- Variable $E_j$ can take multiple values $e_{jk}$, so on averaging:
Proporties:
Expected value of information is always non-negative:
VPI is not additive:
VPI is order independent:
Design a new agent
Agent should gather information before taking actions, if possible.